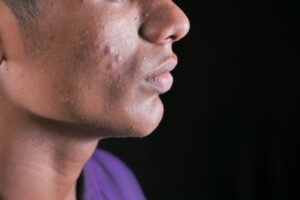
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often mistaken for acne or persistent redness. It tends to appear on the central face, particularly the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead.
Unlike acne, rosacea is not caused by clogged pores or bacteria. It involves a combination of vascular sensitivity, immune response, and inflammation. Flare-ups can come and go, often triggered by heat, alcohol, spicy food, or stress. While there is no permanent cure, symptoms can be controlled with the right care, medications, and trigger management.
What Causes Rosacea
Researchers have not identified a single cause of rosacea, but several factors play a role:
-
Genetics: people with fair or sensitive skin are more prone.
-
Immune response: overactive immune reactions can lead to chronic redness and inflammation.
-
Demodex mites: naturally present on skin, but overgrowth can worsen rosacea.
-
Vascular changes: fragile blood vessels can dilate easily, leading to visible redness.
-
Environmental triggers: UV exposure, temperature shifts, alcohol, spicy food, and stress can all cause flare-ups.
Types of Rosacea
There are four main clinical types of rosacea, and some people experience overlap:
-
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): persistent redness and visible capillaries.
-
Papulopustular Rosacea: red bumps and pustules that resemble acne, but without blackheads or whiteheads.
-
Phymatous Rosacea: thickened skin, often on the nose, known as rhinophyma.
-
Ocular Rosacea: affects the eyes, causing dryness, irritation, and swelling of the eyelids.
Common Symptoms
Rosacea symptoms can vary, but often include:
-
Facial redness and flushing
-
Visible small blood vessels
-
Burning or stinging sensations
-
Dry, sensitive, or rough skin
-
Small red bumps that resemble acne
-
Eye irritation or dryness
Common Rosacea Triggers
Managing rosacea means learning what causes flare-ups. The most common triggers include:
-
Direct sun exposure
-
Hot drinks or spicy food
-
Alcohol, especially red wine
-
Heat, saunas, or humidity
-
Stress and emotional changes
-
Harsh skincare ingredients
-
Hormonal fluctuations
Keeping a trigger diary can help identify patterns unique to you.
How Rosacea Differs from Acne
Although rosacea and acne may look similar, they behave very differently. Rosacea involves inflammation and blood vessel changes, not clogged pores. It also lacks blackheads and whiteheads.
Common acne treatments like benzoyl peroxide or strong exfoliating acids can actually worsen rosacea. Instead of drying out the skin, rosacea care focuses on calming inflammation and strengthening the skin barrier.
Proven Treatment Options
Topical treatments
-
Metronidazole gel or cream: reduces inflammation and redness.
-
Azelaic acid 15–20%: helps reduce both redness and bumps.
-
Ivermectin cream (Soolantra): targets Demodex mites and inflammation.
-
Brimonidine or oxymetazoline gel: temporarily reduces visible redness by narrowing blood vessels.
Oral medications
-
Low-dose doxycycline: reduces inflammation without strong antibiotic effects.
-
Isotretinoin (for severe cases): used under strict medical supervision.
Laser and light therapies
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) and Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) can reduce redness and visible vessels over time.
Skincare for Rosacea
A gentle skincare routine can make a significant difference in controlling rosacea symptoms.
Do:
-
Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
-
Moisturize daily with calming ingredients like niacinamide and ceramides.
-
Apply broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher every day.
Avoid:
-
Alcohol-based toners.
-
Harsh scrubs or exfoliants.
-
High concentrations of glycolic or salicylic acid.
-
Essential oils or heavy fragrances.
Recommended Skincare Products for Rosacea-Prone Skin
-
La Roche-Posay Toleriane Hydrating Gentle Cleanser – non-foaming and soothing for dry, sensitive skin.
-
CeraVe Redness Relief Cleanser – gentle foaming gel that calms redness and irritation.
-
Avene Antirougeurs Calm Soothing Mask – formulated specifically for redness-prone skin.
-
Eucerin Redness Relief Night Cream – licorice root extract helps calm visible redness.
-
EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46 – lightweight, oil-free sunscreen with niacinamide and zinc oxide.
Rosacea Lifestyle Management
-
Track triggers and avoid them when possible.
-
Protect your face from sunlight and temperature extremes.
-
Manage stress with relaxation or breathing techniques.
-
Avoid hot beverages, spicy food, and alcohol if they cause flare-ups.
-
Apply sunscreen every morning, even indoors if near windows.
Consistency matters more than perfection. Rosacea management is about reducing triggers and maintaining balance.
FAQ About Rosacea
Can rosacea go away on its own?
No, rosacea does not disappear completely, but symptoms can be managed effectively with consistent care and treatment.
Can untreated rosacea cause permanent redness?
Yes. Repeated inflammation can lead to dilated blood vessels that remain visible even after flare-ups end. Early treatment can minimize this long-term effect.
Can people with rosacea use chemical exfoliants at all?
In small amounts, yes. Very low-strength lactic acid or PHA formulas may improve texture if used once a week. Always patch-test and discontinue if burning occurs.
Can rosacea and acne occur together?
Yes, it is possible to have both. Your dermatologist may prescribe a tailored plan that calms redness and targets breakouts simultaneously.
What foods trigger rosacea flare-ups?
Common triggers include alcohol, spicy food, hot drinks, and histamine-rich foods such as aged cheese or processed meats.
Is rosacea linked to gut health?
Emerging studies suggest a possible connection between rosacea and gut conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Treating digestive imbalance under medical guidance may help reduce inflammation for some patients.
Can makeup help hide rosacea safely?
Yes. Choose fragrance-free, mineral-based, or green-tinted primers that neutralize redness. Avoid waterproof or heavy matte formulas that require harsh removal. Always remove makeup gently with a mild cleanser.
Can skincare routines make rosacea worse even if products are gentle?
Yes. Over-cleansing, frequent product switching, or using too many active ingredients at once can overwhelm sensitive skin. Rosacea responds best to a short, consistent routine with minimal products.
Does weather affect rosacea symptoms?
Absolutely. Both hot and cold extremes can cause flushing. In winter, indoor heating dries the skin and increases redness, while summer humidity and heat can dilate vessels. Using a humidifier in winter and wearing SPF year-round helps keep balance.
Can stress really trigger rosacea flare-ups?
Yes. Emotional stress activates hormones that increase blood flow and inflammation. Relaxation techniques such as slow breathing, yoga, or short daily walks can visibly reduce frequency of flares over time.
Can rosacea appear on the body or only the face?
While facial redness is most common, rosacea can occasionally appear on the neck, chest, or scalp. In those areas, dermatologists often recommend the same calming treatments used for facial rosacea.